In today’s fast-paced digital world, people expect websites to load quickly. If a website takes too long to load, visitors are likely to abandon it and go to a competitor’s site. Therefore, website loading speed is a critical factor in user experience (UX), which has a direct impact on website traffic, engagement, and conversion rates.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss the importance of website loading speed for UX, how it affects website performance, and what you can do to optimize it.
What is Website Loading Speed?
Website loading speed or page speed refers to the amount of time it takes for a website to load its content fully. It’s measured in seconds or milliseconds and includes several factors such as server response time, file size, and the number of requests.
Why is Website Loading Speed Important for UX?
Website loading speed is a crucial factor for UX because it directly affects user engagement, satisfaction, and conversion rates. Here are some reasons why:
- User Experience: Users expect websites to load quickly, and if they don’t, they’re likely to leave. Slow page speed can lead to a poor user experience, which can result in a high bounce rate, low time on site, and low engagement
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Page speed is a ranking factor in search engine algorithms. If your website has a slow page speed, it’s less likely to rank high in search engine results pages (SERPs), which can result in less traffic and fewer leads.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Mobile devices have limited processing power and network connectivity, so mobile users are even more sensitive to page speed than desktop users. Therefore, if your website isn’t optimized for mobile devices, it can result in a poor user experience and lost traffic.
- Conversion Rates: Slow page speed can also have a direct impact on conversion rates. Studies show that a one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions. Therefore, optimizing page speed can lead to higher conversion rates and more revenue.
How Does Website Loading Speed Affect Website Performance?
Slow Website loading affects website performance in several ways, including:
- Bounce Rate: Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only one page. Slow page speed can increase bounce rates, indicating that visitors are not finding what they’re looking for quickly enough.
- Time on Site: Time on site refers to the amount of time a visitor spends on a website. Slow page speed can decrease time on site, indicating that visitors are not engaging with the content or finding it relevant enough.
- Page Views: Page views refer to the number of pages a visitor views during a session. Slow page speed can decrease page views, indicating that visitors are not interested in exploring the website further.
- Conversion Rates: Conversion rates refer to the percentage of visitors who take a desired action on a website, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. Slow page speed can decrease conversion rates, indicating that visitors are not willing to wait for the website to load or that they don’t trust the website’s reliability.
How to Improve Website Loading Speed for Better UX?
To improve website loading speed for UX, you can do the following:
- Minimize HTTP Requests: HTTP requests refer to the number of requests a website makes to load its content. The more requests a website makes, the slower it will load. You can reduce HTTP requests by minimizing the number of images, scripts, and stylesheets.
- Compress Images: Large images can slow down page speed significantly. You can compress images to reduce their file size without sacrificing quality. You can use tools like Kraken.io, TinyPNG, or ImageOptim to compress images.
- Use Browser Caching: Browser caching: Browser caching is a technique that allows a website to store some of its resources on a user’s device, such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files. When a user visits a website for the first time, their browser downloads all the resources required to display the website. With browser caching, the browser stores these resources so that they can be reused the next time the user visits the website. This reduces the number of requests made to the server, resulting in faster page load times.
- Remove any unused plugins: When you are using WordPress, it’s simple to get carried away when building or owning your first website and add as many plugins as you like. You usually anticipate using these plugins in the near future, but that hasn’t happened, has it? Instead, such unneeded plugins damage the pace at which your website loads. So, get rid of any unnecessary plugins as quickly as you can.
- Minify Code: Minification is the process of removing unnecessary characters, such as white space and comments, from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. This reduces the size of the files, resulting in faster page load times. You can use tools like HTMLMinifier, CSSNano, and UglifyJS to minify code.
- Get rid of 404 errors: Broken files or files with error 404 slow down page loads by overloading your server. Furthermore, 404 errors can significantly lower your chances of converting a consumer since they leave them unsure of how to continue their informational or purchasing journey. We advise employing detection tools, such as Google Search Central, or plugins (such as Rank Math or Yoast SEO) that can identify broken links and display the notice to prevent 404 errors. From there, you may choose to eliminate all of the links, redirect them, or keep them in place (if there is no traffic on the page).
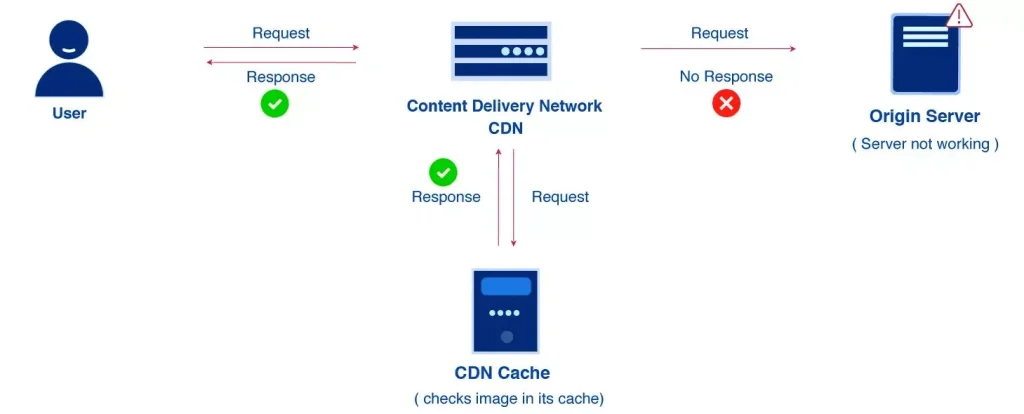
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN is a network of servers that are located in different parts of the world. When a user requests a resource from a website, the CDN delivers the resource from the server that is closest to the user. This reduces the distance that the data needs to travel, resulting in faster page load times. Popular CDNs include Cloudflare, Akamai, and Amazon CloudFront.
- Reduce Redirects: Redirects hurt load times and SEO. To display visitors the necessary material, the redirects route them across various pages. Think about it: if it takes one page four seconds to load, three pages must take twelve seconds to load. To prevent this, periodically check your website to determine whether it has any redirects—on the website pages or plug-ins—or if it links to any other websites that do. To find out which redirects are hurting your site, utilize Google PageSpeed.
- Optimize Web Hosting: Your web hosting provider can also have an impact on page speed. Choose a hosting provider that offers fast and reliable servers, as well as caching and optimization features.
Read More: 25 Best SEO Audit Tools in 2023 – [Free + Paid SEO Tools]
Conclusion
In conclusion, page speed is a critical factor for user experience, and it directly affects website performance, traffic, engagement, and conversion rates. Slow page speed can lead to a poor user experience, high bounce rates, low time on site, and low conversion rates.
Therefore, it’s essential to optimize page speed by minimizing HTTP requests, compressing images, using browser caching, minifying code, using a CDN, and choosing a fast and reliable web hosting provider. By doing so, you can improve user experience, increase engagement and conversion rates, and ultimately drive more revenue for your business.